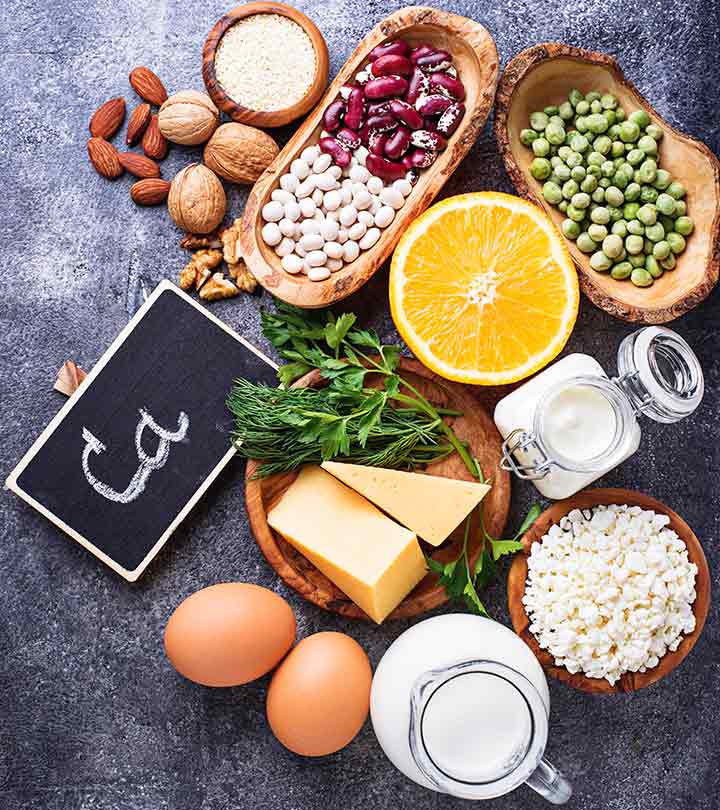
As the most abundant mineral in your body, calcium is essential for your body’s overall nutrition and health. Calcium makes up approximately 2 percent of your total body weight and contributes to many basic body functions, including disease prevention and absorption of other nutrients. Consuming enough calcium — between 1,000 and 1,200 milligrams per day for healthy men and women — is a must for optimal nutrition and health.
Basic Functions
Calcium performs a number of basic functions in your body. Your body uses 99 percent of its calcium to keep your bones and teeth strong, thereby supporting skeletal structure and function. The rest of the calcium in your body plays key roles in cell signaling, blood clotting, muscle contraction and nerve function. Cells use calcium to activate certain enzymes, transport ions across the cellular membrane, and send and receive neurotransmitters during communication with other cells. As an electrolyte, or a particle that helps conduct electricity in the body, calcium is also one of the key players in maintaining a regular heartbeat.
Nutrient Interactions
Calcium can affect how your body absorbs and uses other nutrients. In nature, calcium carries a very small electrical charge, which is why it can conduct electricity within your body. Because your body only absorbs a certain number of charged particles at once, the presence of calcium may cause a temporary lower absorption rate of other naturally charged minerals, such as iron, zinc and magnesium. The decreased absorption of these minerals may not be severe enough to cause nutritional deficiencies, but healthcare professionals recommend consuming any supplements of these minerals at least 2 hours before or after you eat calcium-rich foods.
Diseases and Conditions
Calcium may decrease the risk for colorectal cancer and can lower systolic blood pressure in individuals with high blood pressure. Additionally, you can decrease your risk for osteoporosis by consuming adequate amounts of calcium throughout your life. Some research also suggests eating calcium-rich foods may decrease your risk for overweight and obesity, although this topic is widely debated within the science community. A study published in a 2004 issue of “Obesity” showed individuals on a high-calcium, high-dairy diet lost 70 percent more body weight than individuals on a low-calcium diet when caloric intake was the same.
Considerations
Consuming too much calcium, especially in the form of calcium supplements, can lead to constipation and kidney stones. The Institute of Medicine recommends healthy men and women limit their daily calcium consumption to 2,000 to 2,500 milligrams. Additionally, other nutrients can affect calcium absorption. Without vitamin D, your body cannot absorb calcium. Caffeine, alcohol and excess sodium can all decrease calcium absorption and/or increase calcium excretion from your body.
Join Us today and Start your Healthy Active Lifestyle Journey. Contact Us now!